Facial trauma can change lives drastically. Imagine waking up unable to smile or eat properly because of an injury to the face. Such trauma is more common than many think, often from car accidents or sports injuries. With the face being a key part of our daily interaction, any injury can significantly impact one’s life.
Early medical intervention plays a crucial role in recovery. The quicker the treatment, the better the chances of regaining full function and appearance. According to statistics, facial injuries account for over 3 million emergency visits each year globally. Knowing what is facial trauma and its impact can encourage us to act promptly.
Let’s explore the basic facts about this condition and increase public awareness about the importance of quick, effective treatment.
Comprehensive Guide to Facial Trauma
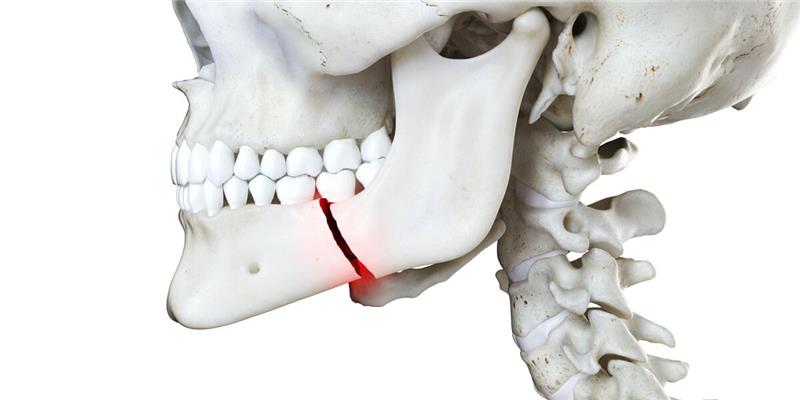
What is facial trauma exactly? It includes any injury to the face or jaw. These injuries often affect both the soft tissues, like skin and muscles, and the bones underneath.
Different types of facial trauma include:
- Soft tissue injuries, such as cuts and bruises.
- Bone injuries, which involve fractures to the jaw, cheekbone, or eye socket.
Knowing the causes can help prevent incidents. Frequent causes include:
- Vehicle accidents: Always wear seatbelts.
- Sports injuries: Helmets and faceguards are vital.
- Interpersonal violence: Prevent altercations when possible.
Recognizing facial trauma symptoms is crucial. These may involve pain, swelling, bruising, or an obvious distortion of facial features. Always seek help if these signs appear.
To properly diagnose facial trauma, medical professionals use both physical exams and imaging tests, like X-rays or CT scans. These help determine the extent and type of injury. Early detection leads to better outcomes, ensuring the best pathway to healing.
Healing and Recovery Process in Facial TraumaThe facial trauma treatment process varies based on injury severity. Modern treatments offer hope, even for severe injuries.
- Soft tissue injuries are usually stitched or treated with specific creams.
- Bone injuries may require resetting or even facial trauma surgery.
Surgical techniques have advanced significantly. They offer a more natural appearance post-recovery and ensure proper function is restored.
Recovery times vary. Minor injuries might heal quickly within weeks. More serious injuries could take months, requiring extensive rehabilitation. Rehabilitation helps restore function, such as speech and facial movements, to normal levels.
Beyond physical healing, psychological support is essential. Many need emotional assistance to cope with changes to their appearance and the anxiety following the trauma. Families and counselors can provide significant support.
Practical post-injury care is important:
- Follow doctor’s guidelines thoroughly.
- Attend all follow-up appointments.
- Report new symptoms immediately.
Keeping the face clean and monitoring any new symptoms ensures complications are managed effectively.
Preventing and Managing Facial Trauma Effectively
Prevention plays a big role in overall facial trauma recovery. Here’s how you can help prevent such injuries:
- Wear protective gear: Helmets or mouthguards during sports can prevent injuries.
- Safe driving habits: Always wear seatbelts and adjust headrests correctly.
- Home safety: Secure loose rugs or furniture to prevent falls.
- Workplace measures: Follow safety guidelines strictly on construction sites.
Knowing when to seek emergency care is vital:
- Immediate help is needed for severe pain, heavy bleeding, or difficulty breathing.
In conclusion, increased public awareness and preventive measures are key. Encourage open conversations about this subject with healthcare providers and in communities. Share this information far and wide, advocating for safety and preparedness. Community education can make a big difference.